Handle AWS SES Bounces and Complaints with AWS Lambda and Terraform

Handling Bounces and Complaints
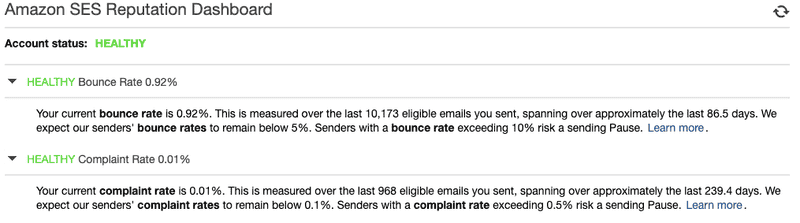
You can use AWS Simple Email Service without handling bounces and complaints even if AWS makes it a requirement. But with the time you can find that your bounces and complaints rates start to grow since the amount of emails that go in nowhere is getting higher.
To not get paused, it is better to stop sending emails to recipients that cause bounces or already marked one of the previous newsletters as spam. Here we have two choices, do it manually or automate the process.
First few months I was doing it manually, by going through messages from MAILER-DAEMON@amazonses.com, finding recipient mail, copying it, and pasting into this array. When I went through all the messages, I would run the script and repeat the process after a few weeks.
After two months of copy-pasting emails, I’ve decided that it is time to automate the process. I’ve written a lambda function that listens for SNS and unsubscribes users from the newsletter and created infrastructure with Terraform that binds everything together.
My goal with this story is to show you how I’ve made this all work together so that you can start handling bounces and complaints in no time. A repository with the Lambda code used in Increaser is here.
AWS Lambda
Let’s got to the repository, open the src folder, and start with the lambda.js file. Here we are exporting a function that handles a request, parses the body, and calls the handler. If something went wrong, it reports errors to Sentry. No matter if there was an error or not, we return the same response since the lambda will be called only by SNS.
Now, lets open handler.js, and we can see that it handles two types of requests. The first type is bounce or complaint, in response to which we are changing the user state in the database. The second type will happen only twice, to confirm that this lambda is responsible for handling bounces and complaints from provided SNS topics.
In sns.js, we have a function that returns a subscribed SNS instance. Lambda located in eu-central-1, but SNS in us-east-1, therefore region specified explicitly.
Domain and topics arns we are getting from environment variables. To deploy code to AWS Lambda, used the script in the management folder. To make AWS CodePipeline understand what to do with the code, we have a configuration file.
Infrastructure
We have lambda in place, and to bind AWS SES with AWS Lambda, we need to create some infrastructure.
locals {
domain = "https://${var.name}.${var.main_domain}"
}
module "lambda" {
source = "git@github.com:radzionc/terraform-pomodoro-lambda.git"
name = "${var.name}"
ci_container_name = "${var.ci_container_name}"
repo_owner = "${var.repo_owner}"
repo_name = "${var.repo_name}"
branch = "${var.branch}"
main_domain = "${var.main_domain}"
zone_id = "${var.zone_id}"
certificate_arn = "${var.certificate_arn}"
env_vars = {
SENTRY_KEY = "${var.sentry_key}"
TOPIC_ARN_BOUNCE = "${aws_sns_topic.bounces-topic.arn}"
TOPIC_ARN_COMPLAINT = "${aws_sns_topic.complaints-topic.arn}"
DOMAIN = "${local.domain}"
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
alias = "virginia"
}
resource "aws_sns_topic" "bounces-topic" {
provider = "aws.virginia"
name = "tf-${var.name}-bounces"
display_name = "bounces"
}
resource "aws_sns_topic" "complaints-topic" {
provider = "aws.virginia"
name = "tf-${var.name}-complaints"
display_name = "complaints"
}
resource "aws_ses_identity_notification_topic" "bounces" {
provider = "aws.virginia"
topic_arn = "${aws_sns_topic.bounces-topic.arn}"
notification_type = "Bounce"
identity = "${var.main_domain}"
include_original_headers = true
}
resource "aws_ses_identity_notification_topic" "complaints" {
provider = "aws.virginia"
topic_arn = "${aws_sns_topic.complaints-topic.arn}"
notification_type = "Complaint"
identity = "${var.main_domain}"
include_original_headers = true
}
resource "aws_sns_topic_subscription" "bounces" {
provider = "aws.virginia"
topic_arn = "${aws_sns_topic.bounces-topic.arn}"
protocol = "https"
endpoint = "${local.domain}/bounce"
endpoint_auto_confirms = "true"
}
resource "aws_sns_topic_subscription" "complaints" {
provider = "aws.virginia"
topic_arn = "${aws_sns_topic.complaints-topic.arn}"
protocol = "https"
endpoint = "${local.domain}/complaint"
endpoint_auto_confirms = "true"
}First, we see a local variable — domain. In Increaser, the name is pomodoro-emails-sns-handler, and the main domain is increaser.org, therefore the domain for AWS Lambda will be https://pomodoro-emails-sns-handler.increaser.org.
Next, we create a lambda with a module that is being used to create multiple services in Increaser. The module described in this story. To make topic arns and domain appear in lambda env vars, we are passing variables to the module.
Other resources will create AWS SNS resources and glue AWS Lambda with AWS SES.
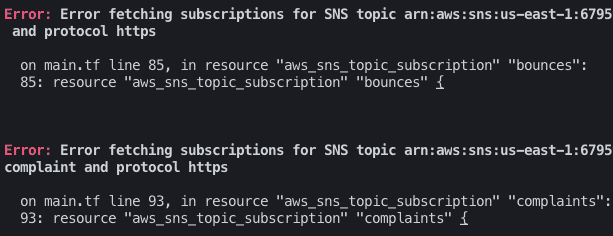
We shouldn’t worry if we see two errors signaling that there are problems with AWS SNS topics. To fix them, we need to deploy code to AWS Lambda first. After doing so, we can run terraform apply again and let the lambda do the work.