Poisson Distribution With Python
March 20, 2018
2 min read

The Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that express the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time, distance, area or volume if these events are independent and the probability that an event occurs in a given length of time does not change through time. Then random variable X, the number of events in a fixed unit of time, has a Poisson distribution. Lambda is an average number of events occurring in the specified period of time.
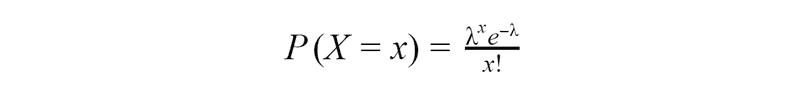
Let’s take a look at the example. Some pizzeria receives an average of 20 orders per hour. Considering that the number of orders in any part of the time is distributed according to Poisson distribution, find the probability that in just two minutes the pizzeria will receive exactly two orders.
As you can see chart have right skewness and probabilities going down after reaching maximum. Poisson distribution will always have right skewness, but it depends on the value of lambda if lambda is large distribution will be close to symmetric. We can show it using the previous example by changing the average number of orders.
Let’s take a look at the characteristics of the Poisson distribution. The mean and the variance:
