Normal Distribution With Python
March 24, 2018
1 min read

The normal distribution is a very important continuous probability distribution because a lot of data can have *almost *normally distributed values. The probability density function for normal distribution looks scary, but we will work only with two parameters — mean and variance.
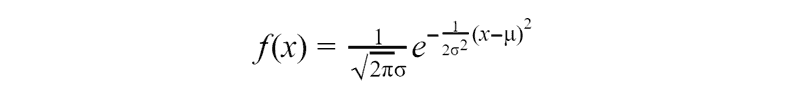
By changing variance we can get quite different distributions. Let’s see for example.
As we increasing standard deviation our distribution becomes “wider”. By changing mean we will “move” distribution because mean in standard deviation equal to the median and it is a peak of the bell curve.
In order to find the probability that value will occur in the specific interval, we should calculate an area of the interval laying under the curve — solve a definite integral. In order to find this integral, we can use numerical analysis magic.