Transportation Problem Balancing with Python
Introduction
Transportation Simplex Method works with a balanced transportation problem. Therefore we need to learn how to make problem balanced if it is not such. And it means to cover two cases — when supply is less than demand and otherwise.
Supply Less Than Demand
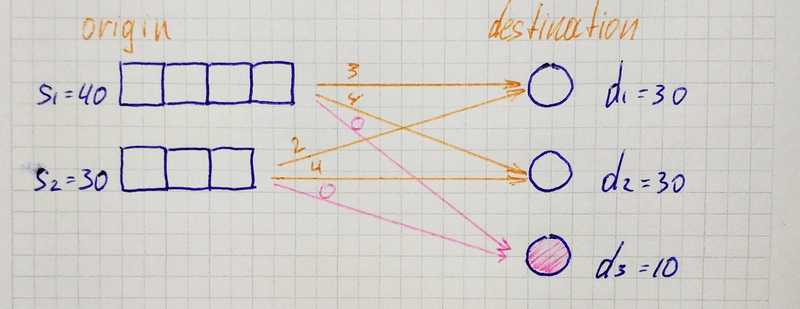
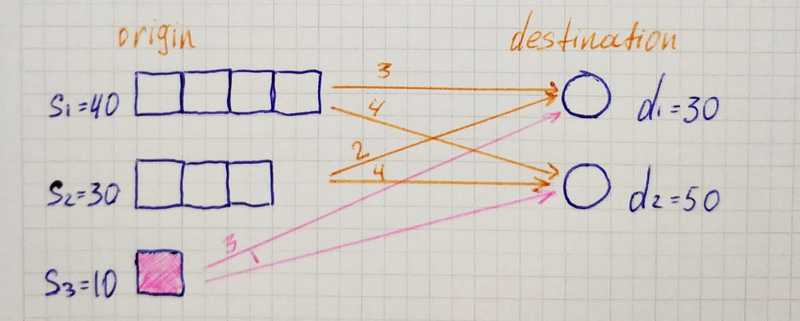
Here we can see that supply is less than demand. In such a case, we add a fake origin (d₃=10) so that supply became equal to demand. Values c₃₁, c₃₂ represent financial loss related to unmet demand.
Demand Less Than Supply
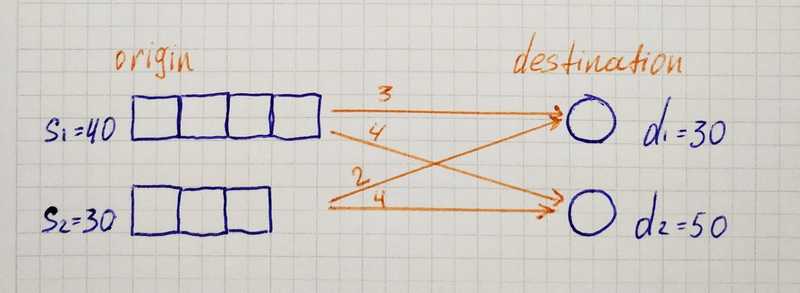
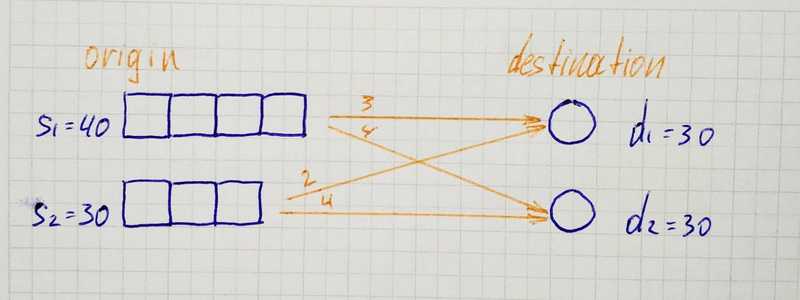
Here we can see that demand is less than supply. In such a case we add a fake destination (s₃ = 1) so that supply became equal to demand. for unused capacity there no cost involved therefor values c₁₃ and c₂₃ are equal to 0.
Programming
Let’s write a simple function that receives a transportation problem and returns its balanced version. When supply less than demand we also need to pass penalties(financial losses related to unmet demands).